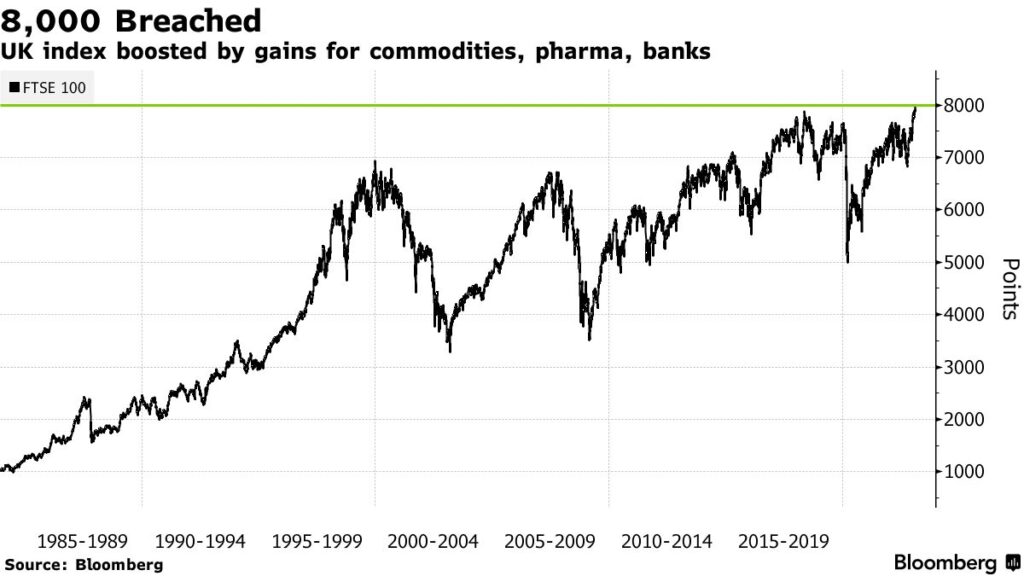
The world of financial trading offers a wide variety of instruments designed to help investors diversify their portfolios, manage risks, and take advantage of opportunities in global markets. Among these instruments, FTSE 100 Futures have become increasingly popular for both beginners and experienced traders who want exposure to the performance of the United Kingdom’s most prominent companies. Understanding how FTSE 100 Futures work, their benefits, risks, and strategies is essential for navigating today’s fast-moving financial environment.
What Are FTSE 100 Futures?
FTSE 100 Futures are derivative contracts based on the FTSE 100 Index, which tracks the performance of the 100 largest companies listed on the London Stock Exchange by market capitalization. These futures contracts represent an agreement to buy or sell the FTSE 100 at a specified price on a future date. Unlike directly buying shares of the companies within the index, trading FTSE 100 Futures allows participants to speculate on the direction of the index as a whole.
The futures are standardized contracts typically traded on recognized exchanges such as the ICE Futures Europe. Each contract is carefully defined, with a clear contract size, expiration dates, and settlement methods. Traders use them for speculation, hedging, or gaining exposure to the broader UK equity market without investing in individual stocks.
Why Trade FTSE 100 Futures?
There are several reasons why traders are attracted to FTSE 100 Futures:
Exposure to the UK Economy
The FTSE 100 Index includes multinational corporations across sectors like finance, energy, healthcare, consumer goods, and technology. By trading futures on this index, participants gain broad exposure to the UK economy and global businesses headquartered in London.
Leverage Opportunities
FTSE 100 Futures allow traders to control a large notional value of the index with a relatively small margin deposit. This leverage magnifies potential profits, but it also increases risks, making careful risk management critical.
Hedging Against Market Risk
Institutional investors and portfolio managers often use FTSE 100 Futures as a hedging tool. For instance, an investor holding a basket of UK equities might short futures contracts to protect against potential downturns in the index.
Liquidity and Transparency
Because the FTSE 100 Index is one of the most closely followed benchmarks in Europe, futures contracts based on it enjoy high liquidity. This ensures tighter spreads, easier execution of trades, and greater transparency in pricing.
Key Features of FTSE 100 Futures
Contract Size
Each FTSE 100 Futures contract has a specific contract size, typically representing £10 per index point. This means that if the index moves by 50 points, the value of the contract changes by £500.
Expiration Dates
Contracts have fixed expiration months, such as March, June, September, and December. Traders need to be aware of these dates to manage open positions or roll them over to later contracts.
Settlement
Most FTSE 100 Futures are cash-settled, meaning no physical delivery of shares occurs. Instead, the difference between the agreed-upon price and the final settlement price of the index is exchanged in cash.
Margin Requirements
Trading FTSE 100 Futures involves margin deposits, which are a fraction of the contract’s total value. Initial margin is required to open a position, while maintenance margin ensures traders keep sufficient funds to cover potential losses.
How to Start Trading FTSE 100 Futures
Step 1: Learn the Basics
Beginners should start by gaining a solid understanding of what futures are, how they differ from stocks, and the specific rules governing FTSE 100 Futures.
Step 2: Choose a Broker
A reliable broker with access to futures markets is essential. Look for brokers that provide competitive commission rates, strong risk management tools, and user-friendly trading platforms.
Step 3: Analyze the Market
Traders should study economic indicators, company earnings, political developments, and global events that may influence the UK equity market. Technical analysis can also help in identifying trends and entry points.
Step 4: Develop a Strategy
No trader should enter the futures market without a well-thought-out strategy. This includes defining goals, setting risk tolerance levels, and determining stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Step 5: Start Small
Beginners are advised to start with a small position size or use demo accounts to practice trading FTSE 100 Futures before committing significant capital.
Trading Strategies for FTSE 100 Futures
Trend Following
This approach involves identifying and trading in the direction of established market trends. For instance, if the index consistently shows upward momentum, traders may buy futures contracts to ride the trend.
Range Trading
Some traders take advantage of sideways markets by buying near support levels and selling near resistance levels. FTSE 100 Futures often display predictable ranges during periods of low volatility.
Hedging Strategies
Portfolio managers may use futures contracts to offset risks from their stock holdings. For example, shorting FTSE 100 Futures can protect long-term investments from short-term declines.
News-Based Trading
The FTSE 100 Index often reacts to breaking news, such as central bank announcements, Brexit-related developments, or global economic reports. Traders use these events as opportunities to capture short-term price movements.
Risks Involved in Trading FTSE 100 Futures
While FTSE 100 Futures present significant opportunities, they also carry risks that traders must manage carefully:
- Leverage Risk: High leverage can amplify both gains and losses. A small adverse movement in the index can lead to substantial losses.
- Market Volatility: Economic or political events can cause sudden and sharp swings in the FTSE 100 Index.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against an open position, traders may face margin calls requiring them to deposit additional funds.
- Emotional Trading: Fear and greed can influence decisions, leading to mistakes such as overtrading or holding losing positions too long.
Practical Tips for New Traders
- Always use stop-loss orders to protect capital.
- Never risk more than a small percentage of your trading account on a single trade.
- Keep a trading journal to track strategies, successes, and mistakes.
- Stay updated with economic calendars and financial news related to the UK and global markets.
- Continuously educate yourself through webinars, trading courses, and market analysis reports.
The Role of FTSE 100 Futures for Experienced Traders
For seasoned investors, FTSE 100 Futures provide advanced opportunities to refine strategies. Experienced traders often use complex techniques such as spread trading, arbitrage, and options-futures combinations to maximize returns. Furthermore, futures markets allow professional traders to act quickly on macroeconomic developments that may affect the UK’s largest companies.
The Future of FTSE 100 Futures
With globalization and increased market interconnectivity, the relevance of FTSE 100 Futures continues to grow. As technology improves access to financial markets, more traders worldwide are expected to participate in UK index futures. Regulatory oversight ensures that trading remains transparent and fair, supporting confidence in these instruments.
Conclusion
FTSE 100 Futures are a vital instrument for anyone interested in gaining exposure to the UK’s premier stock market index. They provide opportunities for speculation, hedging, and portfolio diversification. Whether you are a newcomer eager to learn or a seasoned professional seeking sophisticated strategies, understanding the mechanics, benefits, and risks of FTSE 100 Futures is essential for trading success. By combining solid knowledge, disciplined strategies, and effective risk management, traders can navigate this dynamic market and potentially achieve long-term growth and profitability.